REST API :
REST : Representational state transfer
API : Application Programming Interface
-> Lightweight approach for communicating between application. It is language independent.
-> Commonly used data format is XML and JSON.Benefits of using spring boot
i) Embedded HTTP server
ii) Create stand-alone Spring applications
iii) Save time on on preparing and configuring the environment
iv) It provides flexible XML configurations, robust batch processing, database transactions, easy workflow, along with a wide variety of tools for development.CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update and Delete, which refers to the following four operations
| HTTP Method | CRUD Operation |
|---|---|
| POST | Create a new entity |
| GET | Read a list of entities or single entity |
| PUT/PATCH | Update an existing entity |
| DELETE | Delete an existing entity |
Comparing JPA to native Hibernate Methods
| Action | Native Hibernate Method | JPA Method |
|---|---|---|
| create/save new entity | session.save() | entityManager.persist() |
| Retrieve entity by id | session.get()/load() | entityManager.find() |
| Retrieve list of entities | session.createQuery() | entityManager.createQuery() |
| Save or Update entity | session.saveOrUpdate() | entityManager.merge() |
| Delete entity | session.delete() | entityManager.remove() |
Tools and technologies used
- Java (Version 8)
- Spring Boot
- JPA
- Maven
- MySql
- Eclipse
- Apache Tomcat
- MySql workbench
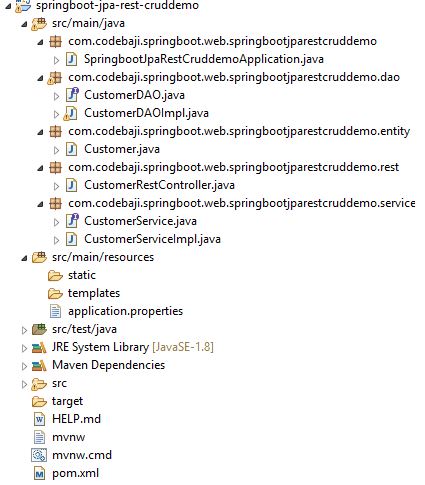
Project Structure
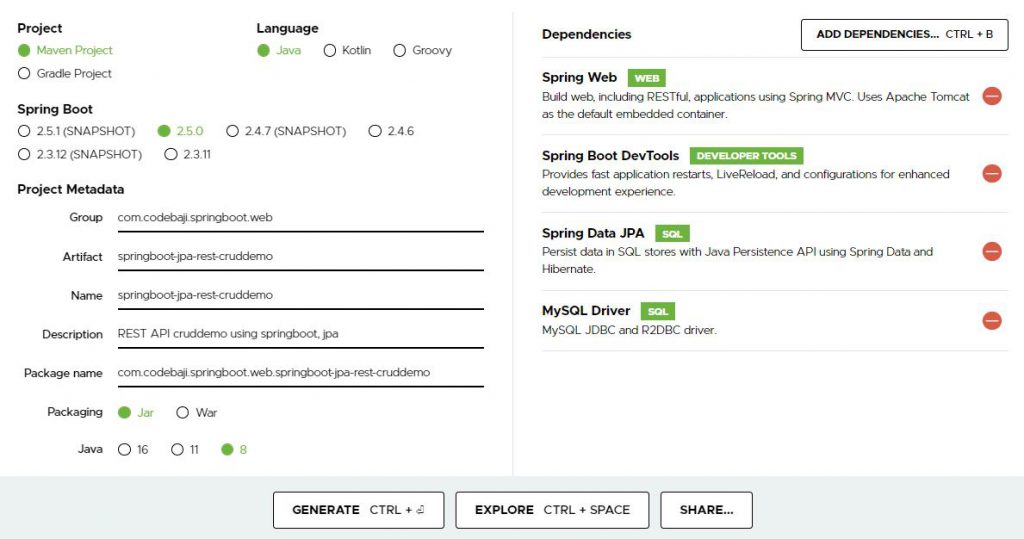
How to create spring boot project
Database Details
Create a database
customer.sql
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `customer_cruddemo`;
USE `customer_cruddemo`;
--
-- Table structure for table `customer`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `customer`;
CREATE TABLE `customer` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`first_name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`last_name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
--
-- Data for table `customer`
--
INSERT INTO `customer` VALUES
(1,'Sachin','Kumar','sachin@codebaji.com'),
(2,'Mohan','Yadav','mohan@codebaji.com'),
(3,'Avani','Patel','avani@codebaji.com'),
(4,'Mayank','Gupta','yuri@codebaji.com'),
(5,'Amar','Singh','amar@codebaji.com');Properties file
Create application.properties in src/main/resources
application.properties
#
# JDBC properties
#
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/customer_cruddemo?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.username=hbcustomer
spring.datasource.password=hbcustomerJar Dependency
Add following dependency in pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>Entity Class
Create entity class in com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.entity
Customer.java
package com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="customer")
public class Customer {
@Id
@Column(name="id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private int id;
@Column(name="first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name="last_name")
private String lastName;
@Column(name="email")
private String email;
public Customer() {
}
public Customer(String firstName, String lastName, String email) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [id=" + id + ", firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email=" + email + "]";
}
}Controller Class
Create Controller class in com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.rest
CustomerRestController.java
package com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.rest;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.entity.Customer;
import com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.service.CustomerService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class CustomerRestController {
@Autowired
private CustomerService customerService;
// expose "/customers" and return list of customers
@GetMapping("/customers")
public List<Customer> findAll(){
return customerService.findAll();
}
// add mapping for GET /customers/{customerId}
@GetMapping("/customers/{customerId}")
public Customer findById(@PathVariable int customerId) {
Customer theCustomer = customerService.findById(customerId);
if(theCustomer == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Customer id not found - " + customerId);
}
return theCustomer;
}
// add mapping for POST /customers - add new customer
@PostMapping("/customers")
public Customer addCustomer(@RequestBody Customer theCustomer) {
// also just in case they pass an id in JSON ... set id to 0
// this is to force a save of new item ... instead of update
theCustomer.setId(0);
customerService.save(theCustomer);
return theCustomer;
}
// add mapping for PUT /customers - update existing customer
@PutMapping("/customers")
public Customer updateCustomer(@RequestBody Customer theCustomer) {
customerService.save(theCustomer);
return theCustomer;
}
// add mapping for DELETE /customers/{customerId} - delete customer
@DeleteMapping("/customers/{customerId}")
public String deleteCustomer(@PathVariable int customerId) {
Customer theCustomer = customerService.findById(customerId);
// throw exception if null
if(theCustomer == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Customer id not found - " + customerId);
}
customerService.deleteById(customerId);
return "Customer employee id - " + customerId;
}
}Data Access Object (DAO) class
Create DAO class in com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.dao
CustomerDAO.java
package com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.dao;
import java.util.List;
import com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.entity.Customer;
public interface CustomerDAO {
public List<Customer> findAll();
public Customer findById(int theId);
public void save(Customer theCustomer);
public void deleteById(int theId);
}CustomerDAOImpl.java
package com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.dao;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.Query;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.entity.Customer;
@Repository
public class CustomerDAOImpl implements CustomerDAO {
// define field for entitymanager
@Autowired
private EntityManager entityManager;
@Override
public List<Customer> findAll() {
// create a query
Query theQuery = entityManager.createQuery("from Customer");
// execute query and get result list
List<Customer> customers = theQuery.getResultList();
// return the results
return customers;
}
@Override
public Customer findById(int theId) {
// get the customer
Customer theCustomer = entityManager.find(Customer.class, theId);
// return the customer
return theCustomer;
}
@Override
public void save(Customer theCustomer) {
Customer newCustomer = entityManager.merge(theCustomer);
theCustomer.setId(newCustomer.getId());
}
@Override
public void deleteById(int theId) {
// delete object with primary key
Query theQuery = entityManager.createQuery("delete from Customer where id=:customerId");
theQuery.setParameter("customerId", theId);
theQuery.executeUpdate();
}
}Service Class
Create Service class in com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.service
CustomerService.java
package com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.service;
import java.util.List;
import com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.entity.Customer;
public interface CustomerService {
public List<Customer> findAll();
public Customer findById(int theId);
public void save(Customer theCustomer);
public void deleteById(int theId);
}CustomerServiceImpl.java
package com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.dao.CustomerDAO;
import com.codebaji.springboot.web.springbootjparestcruddemo.entity.Customer;
@Service
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService {
@Autowired
private CustomerDAO customerDAO;
@Override
@Transactional
public List<Customer> findAll() {
return customerDAO.findAll();
}
@Override
@Transactional
public Customer findById(int theId) {
return customerDAO.findById(theId);
}
@Override
@Transactional
public void save(Customer theCustomer) {
customerDAO.save(theCustomer);
}
@Override
@Transactional
public void deleteById(int theId) {
customerDAO.deleteById(theId);
}
}Details of annotations used in this project
- @Entity : The @Entity annotation specifies that the class is an entity and is mapped to a database table.
- @Table : The @Table annotation specifies the name of the database table to be used for mapping.
- @Id : The @Id annotation specifies the primary key of an entity.
- @Column : The Column annotation is used to specify the mapped column for a persistent property or field. If no Column annotation is specified, the default value will be applied.
- @GeneratedValue : @GeneratedValue provides for the specification of generation strategies for the values of primary keys.
- @Override : The @Override annotation indicates that the child class method is over-writing its base class method.
- @RestController : Spring RestController takes care of mapping request data to the defined request handler method. It is Extension of @Controller. Handles REST requests and responses.
- @RequestMapping : The @Entity annotation specifies that the class is an entity and is mapped to a database table. It maps HTTP request with a path to a controller method.
- @Autowired : It marks a constructor, field, or setter method to be autowired by Spring dependency injection.
- @GetMapping : It handles the HTTP GET requests matched with given URI expression. It is a shortcut for @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET).
- @PostMapping : It maps HTTP POST requests onto specific handler methods. It is a composed annotation that acts as a shortcut for @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST).
- @PutMapping : It is used for mapping HTTP PUT requests onto specific handler methods. Specifically, @PutMapping is a composed annotation that acts as a shortcut for @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT).
- @DeleteMapping : @DeleteMapping annotation maps HTTP DELETE requests onto specific handler methods. It is a composed annotation that acts as a shortcut for @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.DELETE).
- @Repository : Indicates that an annotated class is a repository, which is an abstraction of data access and storage.
- @Service : It indicates that an annotated class is a service class. @Service annotation is used with classes that provide some business functionalities.
- @Transactional : It minimize(eliminate) code to manually stopping and starting transaction.
- @RequestBody : Used to access the request body as POJO. It binds POJO to a method parameter.
- @PathVariable : It indicates that a method parameter should be bound to a URI template variable.